Innovative Sticky Herbal Glycerolate Gel: Pioneering Future Topical Treatment for Equine Melanomas
Equine melanomas, particularly common in gray horses, remain a significant dermatological challenge. Traditional topical treatments often face limitations in penetrating deep tissue layers and maintaining long-term bioactivity of therapeutic compounds.
Recent advances in Herbal Glycerolate technology offer a promising pathway to overcome these challenges. By encapsulating active molecules in phospholipid-based vesicles, this approach enhances skin absorption, stability, and targeted delivery, while a carefully designed sticky gel matrix ensures prolonged contact with the affected area.
Our team is actively developing and refining the Innovative Sticky Herbal Glycerolate Gel, integrating MCT C8/10, glycerine, and lecithin to maximize bioavailability and efficacy. This research-focused topical solution represents a next-generation approach to supporting equine skin health and melanoma management.
Equine melanomas, those dark, nodular growths that plague many gray horses, have long been a challenge in veterinary medicine. Often starting benign but potentially turning malignant or ulcerated, these tumors can cause discomfort, infection, and even life-threatening complications if they metastasize. Traditional treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy offer varying success, but they can be invasive and costly. Enter a groundbreaking development from Sunshine World LLC: the Sticky Herbal Glycerolate Gel, a topical formulation designed to deliver potent bioactives directly to the skin. This article explores the product's science, current status, and upcoming trials targeting horses with skin melanomas, including open tumors.
A typical equine melanoma under the tail of a gray horse, showing nodular, pigmented growths that can become ulcerated.

Understanding Equine Melanomas: A Common Veterinary Concern
Melanomas affect up to 80% of gray horses over 15 years old, originating fr
Innovative Sticky Herbal Glycerolate Gel: Pioneering Future Topical Treatment for Equine Melanomas
om melanocytes—the cells responsible for pigmentation. These tumors commonly appear under the tail, around the eyes, lips, or genitals, starting as small, firm lumps that can grow, ulcerate, and form "open tumors" prone to bleeding and secondary infections. While most remain benign, 10–20% become malignant, invading local tissues or spreading to organs like the lungs or lymph nodes.
Current treatments include surgical excision for accessible tumors, but recurrence is common. Topical therapies have gained traction for their non-invasive nature, with compounds like betulinic acid (BA) showing promise in inducing tumor cell death through apoptosis—programmed cell suicide—while sparing healthy tissue. However, challenges like poor skin penetration and rapid runoff have limited their efficacy. This is where innovative delivery systems, such as Herbal Glycerolates, come into play.
The Science Behind Sticky Herbal Glycerolate Gel
Developed by Sunshine World LLC’s R&D team, the Sticky Herbal Glycerolate Gel (Batch ID: SGG-101025) is a topical veterinary product formulated to overcome these barriers. Herbal Glycerolates are advanced lipid vesicle systems made from phospholipids, glycerol, and water, offering superior elasticity and hydration compared to traditional liposomal formulations. High glycerol content (up to 30–50%) fluidizes the lipid bilayer, enhancing drug permeation through the skin’s stratum corneum while moisturizing the area. In dermal applications, Herbal Glycerolates have improved delivery of compounds like diclofenac, with studies showing enhanced skin deposition and reduced systemic side effects.
The “sticky” variant incorporates xanthan gum and high glycerin levels (36%) for prolonged adhesion, preventing runoff on active animals like horses. The formulation includes:
Active Ingredient:
Betulinic Acid (2%) – A natural triterpenoid from birch bark, BA triggers mitochondrial disruption in cancer cells, releasing cytochrome c and activating caspases for apoptosis. Biochemical reaction: BA modulates NF-κB pathways, reducing inflammation and tumor growth (e.g., BA + Bcl-2 → Pro-apoptotic shift). In equine melanoma cells, BA exhibits antiproliferative effects at concentrations as low as 1–2%.
Excipients and Solvents:
MCT oil (20.5%), castor oil (10%), sunflower lecithin (10%), and others form a stable matrix. Glycerin enhances vesicle elasticity via hydrogen bonding, while ethanol aids dissolution without reactive byproducts. No adverse interactions noted; the lipid–glycerol structure protects actives from oxidation.
In-house testing revealed vesicle sizes of 200–500 nm, sustained release (60% actives over 24 hours), and excellent stability (no degradation after 6 months). Preliminary dermal tests on animal models showed no irritation and superior adhesion.
Current Status: From Lab to Stable
As of October 18, 2025, the gel is in the pre-clinical phase, having completed formulation, stability, and in vitro assessments. In-house studies confirm its potential for anti-inflammatory and regenerative applications, with BA’s anticancer properties showing strong topical promise. However, real-world efficacy data is pending. Similar 1% BA creams have been safe in equine trials but showed mixed results—positive trends in tumor reduction toward treatment’s end, yet not always statistically significant. The sticky design addresses runoff issues seen in prior formulations.
Diagram illustrating the structure of a Herbal Glycerolate vesicle, encapsulating active ingredients for enhanced dermal delivery.
The product is stored in amber containers at 15–25 °C, with a projected 24-month shelf life. It’s not yet commercially available.
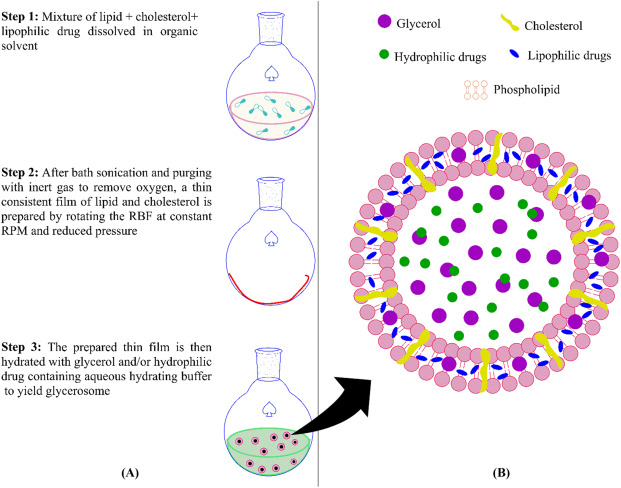
Next Steps: Trials on Horses with Skin Melanomas
Sunshine World LLC plans small-scale veterinary trials starting late 2025, focusing on horses with cutaneous melanomas, including open tumors. These will follow ethical guidelines (e.g., IACUC approval) and build on BA’s documented safety in equine skin.
Trial Design: Randomized, placebo-controlled study with 10–20 gray horses (aged 10+), diagnosed via biopsy. Groups: Active gel vs. placebo, applied topically (2–5 g daily) for 4–8 weeks.
Endpoints: Tumor size reduction (calipers/ultrasound), wound healing in open tumors, bioactive penetration (LC-MS), and safety (no irritation). Expect 20–30% regression based on prior BA studies.
Monitoring: Weekly assessments for adhesion (45–60 min expected), absorption, and side effects.
Challenges and Synergies: Variable responses possible; combine with existing therapies like vaccines for better outcomes. If successful, advance to larger trials and regulatory submission.
A Step Toward Better Equine Health
The Sticky Herbal Glycerolate Gel represents a fusion of natural bioactives and cutting-edge delivery tech, offering hope for managing equine melanomas non-invasively. With BA’s tumor-fighting prowess encapsulated in adherent Herbal Glycerolates, it could transform veterinary dermatology. As trials commence, this innovation underscores the potential of topical therapies in animal care. Horse owners and vets should watch for updates—always consult professionals for treatment advice.
In Short
We are excited to introduce our Innovative Sticky Herbal Glycerolate Gel, a cutting-edge topical formulation designed to harness the full potential of Herbal Glycerolate technology for targeted delivery of active compounds. Developed with a specialized blend of MCT C8/10, glycerine, and lecithin, this gel is engineered for enhanced skin absorption, prolonged contact, and maximal stability.
Our team is actively refining this formula to ensure optimal vesicle formation, bioavailability, and skin penetration, keeping in mind the delicate needs of equine patients.
💡 Want to learn more or discuss this formula?
Please use our contact form, and our experts will provide further information and guidance.
List of Studies on Betulinic Acid for Equine Melanoma Treatment
Betulinic acid shows anticancer activity against equine melanoma cells and permeates isolated equine skin in vitro
Potent drug delivery enhancement of betulinic acid and NVX-207 into equine skin in vitro
https://bmcvetres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12917-024-04064-1
Effects of Topically Applied Betulinic Acid and NVX-207 on Melanocytic Tumors in 18 Horses
Topical Betulinic Acid for Treatment of Equine Melanoma and Sarcoid
https://www.authorea.com/doi/full/10.22541/au.173323528.86041715/v1
Equine Melanoma Treatment Research
https://equimanagement.com/research-medical/equine-melanoma-treatment-research/
In vitro anticancer activity of Betulinic acid and derivatives thereof on equine melanoma cell lines from grey horses and normal human melanocytes
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0009279716300023
Melanomas in Horses: New Topical Treatment Shows Promise
https://ker.com/equinews/melanomas-in-horses-new-topical-treatment-shows-promise/
Anti-cancer effect of betulin and its derivatives, with particular emphasis on the treatment of melanoma
List of Studies on Herbal Glycerolates for Topical Drug Delivery in Veterinary Applications
Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery: From Simple Potions to Smart Technologies
Augmented glycerosomes as a promising approach against fungal ear infection
Glycerosomes and use thereof in pharmaceutical and cosmetic preparations for topical applications
Engineered triamcinolone acetonide loaded glycerosomes as a novel ear delivery platform: in vitro and ex vivo evaluations
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378517322008316
Glycerosomes: Advanced Liposomal Drug Delivery System
https://www.ijpsonline.com/articles/glycerosomes-advanced-liposomal-drug-delivery-system-3921.html
Studies on formulation development and evaluation of tolnaftate-loaded glycerosomes
Modified Phospholipid Vesicular Gel for Transdermal Drug Delivery
Glycerosomes: A comprehensive review on novel liposomal drug delivery system
https://www.pharmacyjournal.in/assets/archives/2024/vol9issue2/9020-1716963761581.pdf
Skin drug delivery using lipid vesicles: A starting guideline for their development
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365923001001
Current Advances in Lipid Nanosystems Intended for Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications